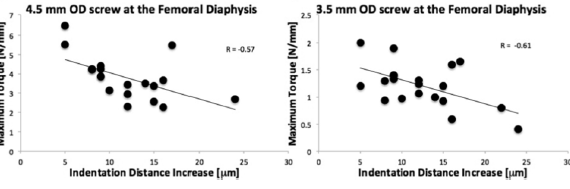
Abstract BACKGROUND: Successful fracture fixation depends critically on the stability of the screw-bone interface. Maximum achievable screw torque reflects the competence of this interface, but it cannot be quantified prior to screw stripping. Typically, the surgeon relies on the patients’ bone mineral density and radiographs, along with experience and tactile […]
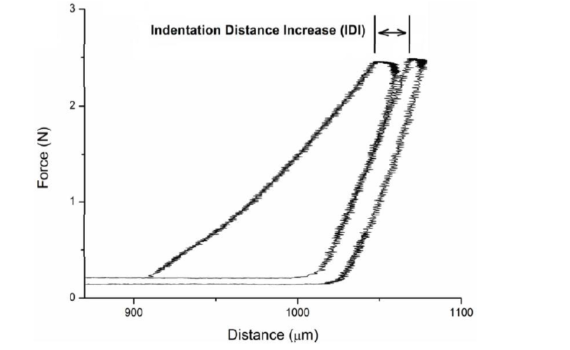
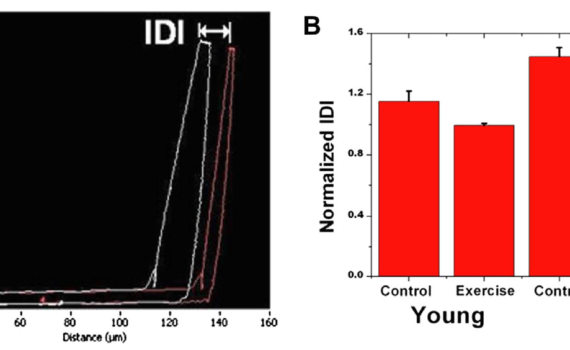
Reference point indentation
Abstract Gap junctions are formed from ubiquitously expressed proteins called connexins that allow the transfer of small signaling molecules between adjacent cells. Gap junctions are especially important for signaling between osteocytes and other bone cell types. The most abundant type of connexin in bone is connexin 43 (Cx43). The C-terminal […]
Abstract The assessment of fracture risk often relies primarily on measuring bone mineral density, thereby accounting for only a single pathology: the loss of bone mass. However, bone’s ability to resist fracture is a result of its biphasic composition and hierarchical structure that imbue it with high strength and toughness. […]
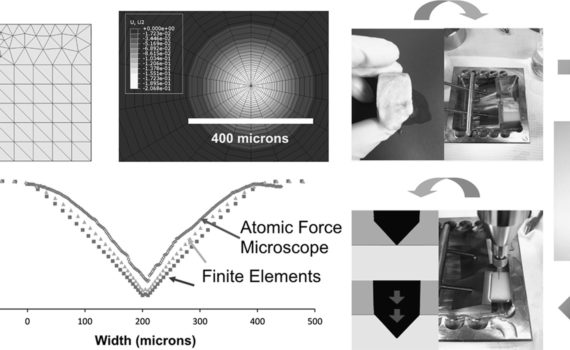
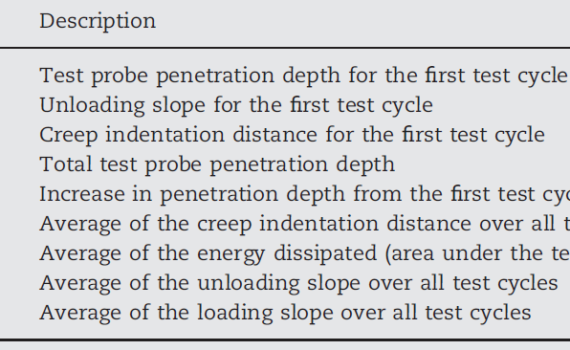
Abstract Reference Point Indentation (RPI) is a novel technique aimed to assess bone quality. Measurements are recorded by the BioDent instrument that applies multiple indents to the same location of cortical bone. Ten RPI parameters are obtained from the resulting force–displacement curves. Using the commercial finite element analysis software Abaqus, […]
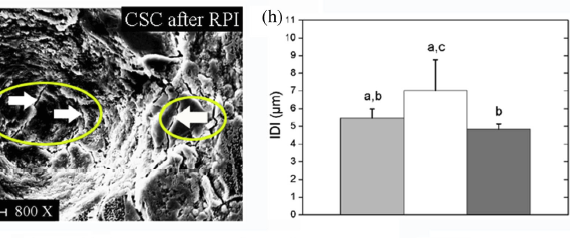
Abstract The objective of this study was to elucidate micromechanical properties of Biodentine and two experimental calcium silicate cements (CSCs) using Reference Point Indentation (RPI). Biomechanical characteristics of the cement type and the effects of a radiopacifier, liquid components, acid etching treatment and bioactivation in simulated body fluid (SBF) were […]
Abstract Reference Point Indentation (RPI) is a novel microindentation tool that has emerging clinical potential for the assessment of fracture risk as well as use as a laboratory tool for straight-forward mechanical characterisation of bone. Despite increasing use of the tool, little research is available to advise the set-up of […]
Abstract Reference Point Indentation (RPI) has been proposed as a new clinical tool to aid the diagnosis of Osteoporosis. This study has examined the performance of the tool within entire femurs to improve the understanding of the mechanical properties of bone and also to guide future RPI testing to optimize […]
Abstract The objective of this study was to determine the effects of various irrigation solutions on root canal dentine and gutta-percha surface properties. In addition, the effects of disinfectant chemicals on the wettability and surface morphological properties of the filling materials were evaluated. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), citric acid, and ozone […]
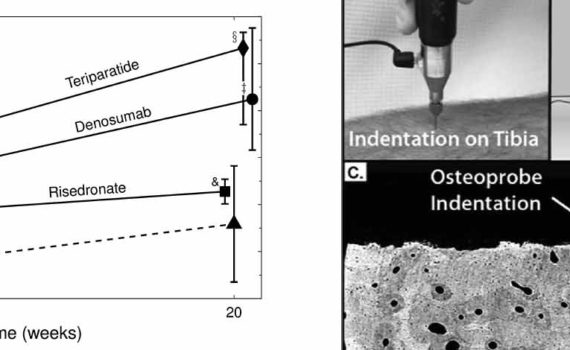
We would like to thank Allen and colleagues for their thorough review of reference point indentation (RPI) for assessing bone mechanical properties in vivo.(1) The authors have focused on two separate RPI devices, the BioDent® and the OsteoProbe®, and have gone to great lengths to compare and contrast these instruments, which differ considerably […]
Abstract In the present study, the possibility that a diabetic (DM) status might worsen age-related bone deterioration was explored in mice. Male CD-1 mice aged 2 (young control group) or 16 months, nondiabetic or made diabetic by streptozotocin injections, were used. DM induced a decrease in bone volume, trabecular number, […]
Abstract Type 2 diabetes (T2D) incidence in adolescents is rising and may interfere with peak bone mass acquisition. We tested the effects of early-onset T2D on bone mass, microarchitecture, and strength in the TALLYHO/JngJ mouse, which develops T2D by 8 weeks of age. We assessed metabolism and skeletal acquisition in […]
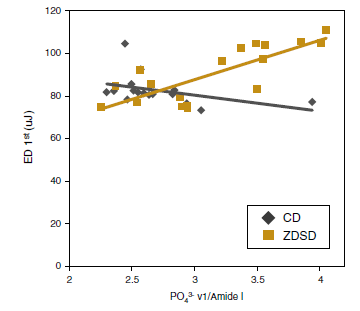
Abstract Diabetes detrimentally affects the musculoskeletal system by stiffening the collagen matrix due to increased advanced glycation end products (AGEs). In this study, tibiae and tendon from Zucker diabetic Sprague-Dawley (ZDSD) rats were compared to Sprague-Dawley derived controls (CD) using Atomic Force Microscopy. ZDSD and CD tibiae were compared using […]
Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta is a congenital disease commonly characterized by brittle bones and caused by mutations in the genes encoding Type I collagen, the single most abundant protein produced by the body. The oim model has a natural collagen mutation, converting its heterotrimeric structure (two α1 and one α2 chains) […]
Comment on In vivo assessment of bone quality in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. [J Bone Miner Res. 2014] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24496824 J Bone Miner Res. 2014 Apr;29(4):784-6. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2189.
Abstract OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to investigate the capability of a novel reference point indentation apparatus to test the indentation properties of root canal surface dentine treated with three intracanal medicaments used in endodontic regeneration. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Immature human premolars were selected (n = 22). Four […]
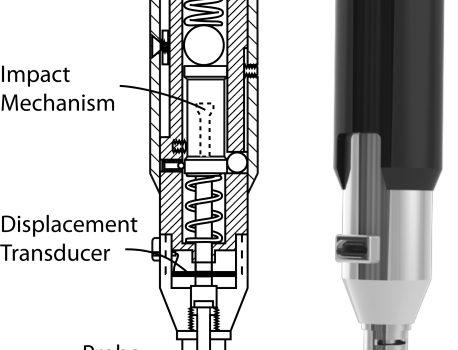
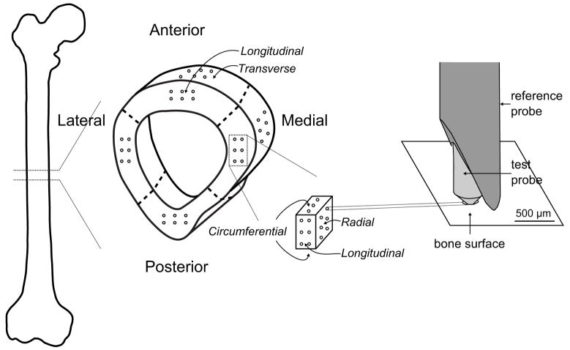
Abstract Here we describe a novel, hand-held reference point indentation (RPI), instrument that is designed for clinical measurements of bone material properties in living patients. This instrument differs from previous RPI instruments in that it requires neither a reference probe nor removal of the periosteum that covers the bone, thus […]
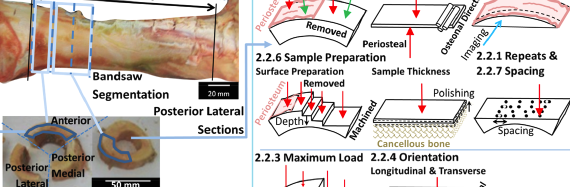
ABSTRACT Characterization of bone is important as it aids in the understanding of bone pathologies and their corresponding treatments. Assessment of cortical bone morphology has been identified as an important aspect of overall bone quality as it contributes significantly to the mechanical strength of bone. In the first part of […]
Abstract Here we describe modifications that allow the bone diagnostic instrument (BDI) [P. Hansma et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 064303 (2008); Rev. Sci. Instrum. 77, 075105 (2006)], developed to test human bone, to test the femora of mice. These modifications include reducing the effective weight of the instrument on […]
Abstract The bone diagnostic instrument (BDI) is being developed with the long-term goal of providing a way for researchers and clinicians to measure bone material properties of human bone in vivo. Such measurements could contribute to the overall assessment of bone fragility in the future. Here, we describe an improved […]
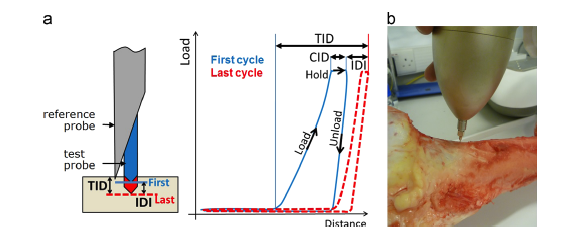
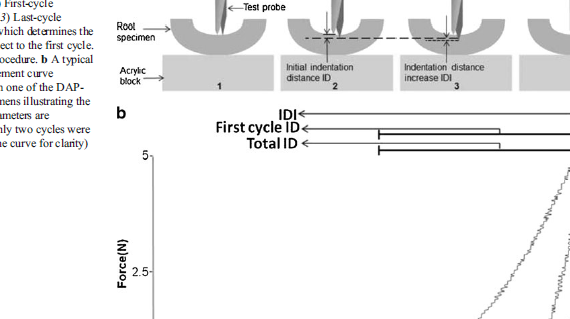
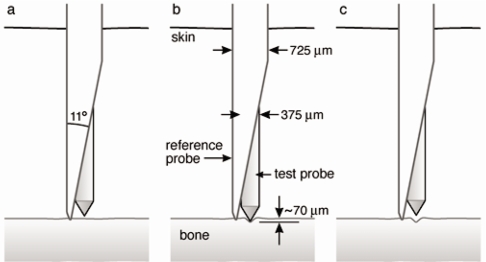
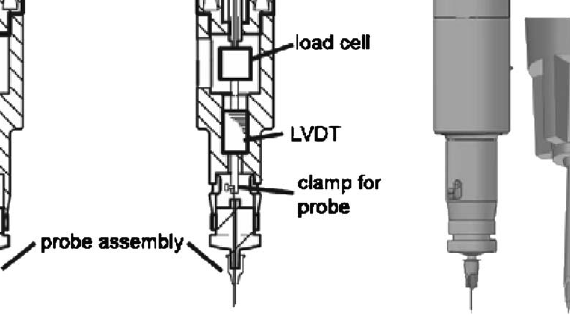
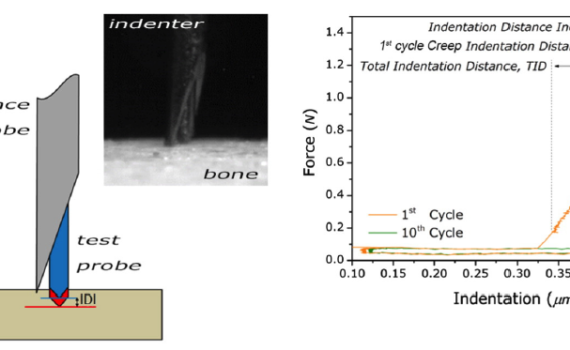
ABSTRACT The bone diagnostic instrument is designed to measure materials properties of bone even if it is covered with soft tissue such as periosteum, connective tissueand skin. It uses (1) a probe assembly, consisting of a reference probe that penetrates soft tissue and stops on the surface of the bone and a test probe that is inserted into the bone, (2) an actuation […]
Abstract BACKGROUND: Bone mineral density (BMD) measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry is used to assess bone health in kidney transplant recipients (KTR). Trabecular bone score and in vivo microindentation are novel techniques that directly measure trabecular microarchitecture and mechanical properties of bone at a tissue level and independently predict fracture […]
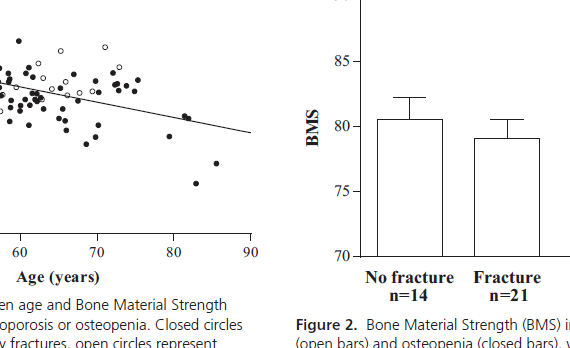
Abstract We evaluated the relationship between bone material strength index (BMSi) and fragility fractures, including vertebral fractures. Our data showed that BMSi is low in all fracture patients with low bone mass, independently of whether patients sustained a vertebral or a non-vertebral fracture. INTRODUCTION: Impact microindentation (IMI) is a new […]
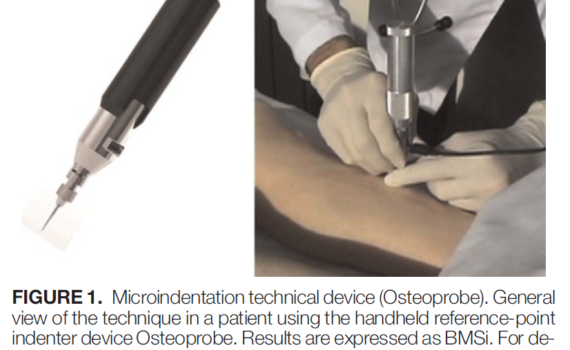
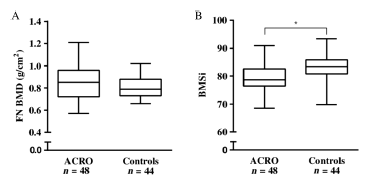
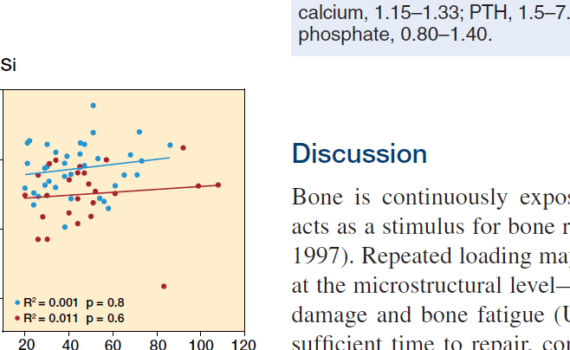
Abstract OBJECTIVE: Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by excess growth hormone (GH) production by the pituitary adenoma. The skeletal complications of GH and IGF-1 excess include increased bone turnover, increased cortical bone mass and deteriorated microarchitecture of trabecular bone, associated with a high risk of vertebral fractures in the […]
Abstract Background and purpose — Bone fragility is determined by bone mass, bone architecture, and the material properties of bone. Microindentation has been introduced as a measurement method that reflects bone material properties. The pathogenesis of underlying stress fractures, in particular the role of impaired bone material properties, is still […]
Abstract Low bone mineral density (BMD) in HIV-infected individuals has been documented in an increasing number of studies. However, it is not clear whether it is the infection itself or the treatment that causes bone impairment. Microindentation measures bone material strength (Bone Material Strength index) directly. We recruited 85 patients, […]
Abstract Densitometry and imaging techniques are currently used in clinical settings to measure bone quantity and spatial structure. Recently, Reference Point Indentation has opened the possibility of directly assessing the mechanical characteristics of cortical bone in living individuals, adding a new dimension to the assessment of bone strength. Impact microindentation […]
Abstract Glucocorticoids, widely used in inflammatory disorders, rapidly increase bone fragility and, therefore, fracture risk. However, common bone densitometry measurements are not sensitive enough to detect these changes. Moreover, densitometry only partially recognizes treatment-induced fracture reductions in osteoporosis. Here, we tested whether the reference point indentation technique could detect bone […]
Abstract CONTEXT: Bone mineral density (BMD) does not fully capture fracture risk as the majority of fractures occur in patients with osteopenia, suggesting that altered bone material properties and changes in microarchitecture may contribute to fracture risk. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between bone material strength (BMS), […]
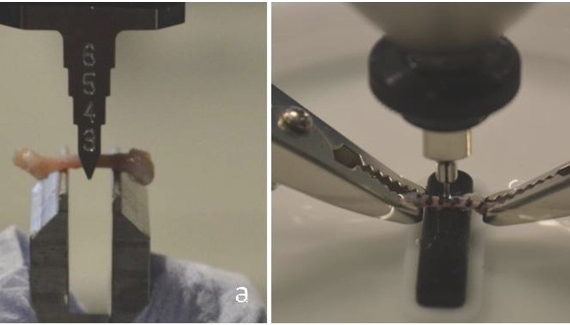
Abstract In an attempt to study the mechanical behavior of bone under indentation, methods of analyses and experimental validations have been developed, with a selected test material. The test material chosen is from an equine cortical bone. Stress-strain relationships are first obtained from conventional mechanical property tests. A finite element […]
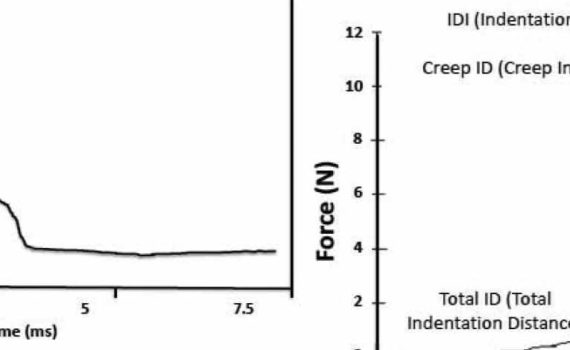
Abstract Reference point indentation (RPI) is a microindentation technique involving 20 cycles of loading in “force-control” that can directly assess a patient׳s bone tissue properties. Even though preliminary clinical studies indicate a capability for fracture discrimination, little is known about what mechanical behavior the various RPI properties characterize and how […]
Abstract We study the reference point indentation (RPI) technique which has a potential to directly measure mechanical properties of bone in patients. More specifically, we tested 6 month swine femoral cortical bone at mid-diaphysis region to investigate the effect of several testing variables on the RPI outputs. They include the […]
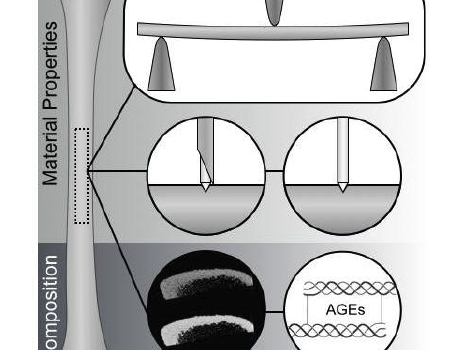
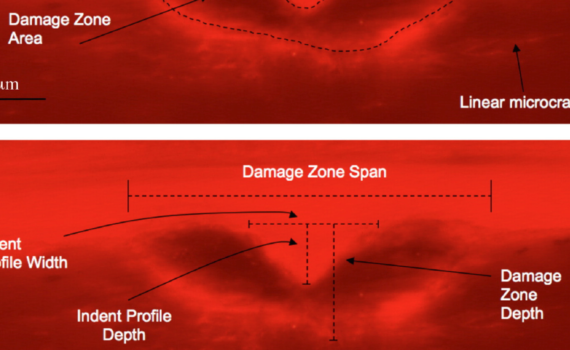
Abstract Limitations associated with current clinical fracture risk assessment tools highlight the need for increased understanding of the fracture mechanisms of the bone and, ideally, a means of assessing this in vivo. Being a multi-layered hierarchical structure, the overall properties of the bone are dictated by its structural and compositional […]
Abstract Bone fragility is a concern for aged and diseased bone. Measuring bone toughness and understanding fracture properties of the bone are critical for predicting fracture risk associated with age and disease and for preclinical testing of therapies. A reference point indentation technique (BioDent) has recently been developed to determine […]
Abstract Measurement of bone mineral density (BMD) is the clinical gold standard in cases of compromised skeletal integrity, such as with osteoporosis. While BMD is a useful measurement to index skeletal health, it is also limited since it cannot directly assess any mechanical properties. The ability to directly assess mechanical […]