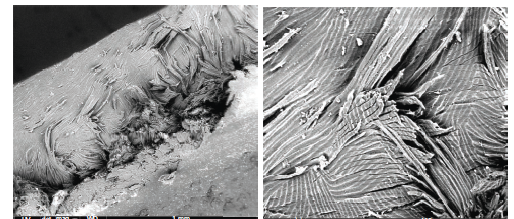
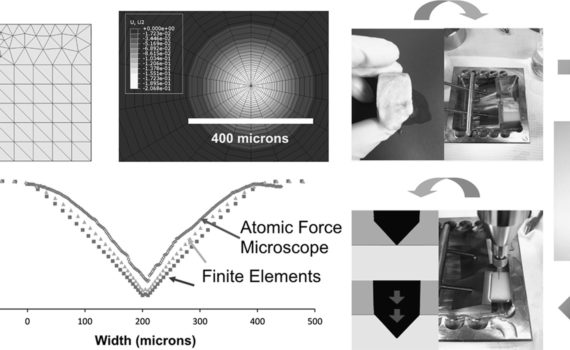
Abstract Two hard botanical structures have been characterised in terms of mechanics and structure: the pseudofruit of Coix lacryma-jobi, a native plant of Southeast Asia, and the kernel of the drupe fruit of Thevetia peruviana, a native plant of tropical America. Two indentation techniques at different scales (micro and nano) were employed. […]
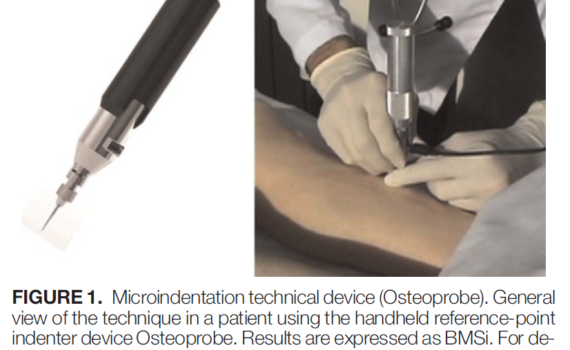
MICROINDENTATION
Abstract Loading increases bone mass and strength in a site-specific manner; however, possible effects of loading on bone matrix composition have not been evaluated. Site-specific structural and material properties of mouse bone were analyzed on the macro- and micro/molecular scale in the presence and absence of axial loading. The response […]
Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta entrains changes at every level in bone tissue, from the disorganization of the collagen molecules and mineral platelets within and between collagen fibrils to the macroarchitecture of the whole skeleton. Investigations using an array of sophisticated instruments at multiple scale levels have now determined many aspects of […]
Abstract Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is generally a very useful tool for assessing bone mineral density (BMD) and fracture risk. However, observational studies have shown that in certain instances, BMD as measured by DXA systematically over- or underestimates fracture risk. We herein describe the clinical conundrums encountered when assessing fracture […]
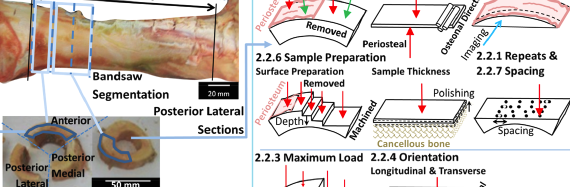
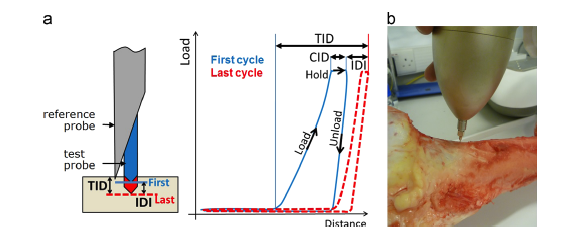
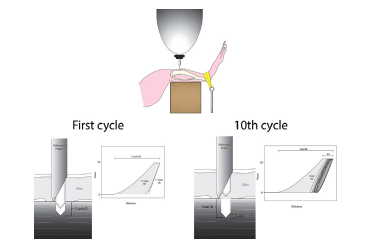
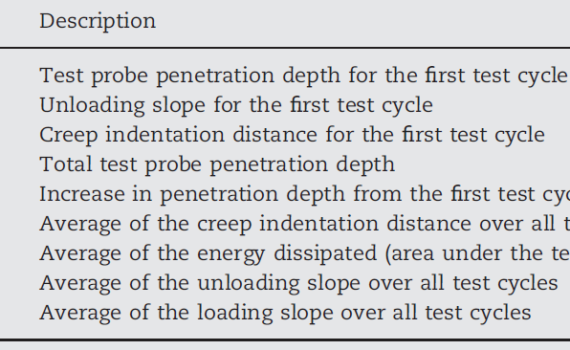
Abstract Reference Point Indentation (RPI) is a novel microindentation tool that has emerging clinical potential for the assessment of fracture risk as well as use as a laboratory tool for straight-forward mechanical characterisation of bone. Despite increasing use of the tool, little research is available to advise the set-up of […]
Abstract Reference Point Indentation (RPI) has been proposed as a new clinical tool to aid the diagnosis of Osteoporosis. This study has examined the performance of the tool within entire femurs to improve the understanding of the mechanical properties of bone and also to guide future RPI testing to optimize […]
Abstract Reference point indentation (RPI) has emerged as a novel tool to measure material-level biomechanical properties in vivo. Human studies have been able to differentiate fracture versus non-fracture patients while a dog study has shown the technique can differentiate drug treatment effects. The goal of this study was to extend this […]
Abstract BACKGROUND: Bone mineral density (BMD) measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry is used to assess bone health in kidney transplant recipients (KTR). Trabecular bone score and in vivo microindentation are novel techniques that directly measure trabecular microarchitecture and mechanical properties of bone at a tissue level and independently predict fracture […]
Abstract Bone health is assessed by bone mineral density (BMD). Other techniques such as trabecular bone score and microindentation could improve the risk of fracture’s estimation. Our chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients presented worse bone health (density, microarchitecture, mechanical properties) than controls. More than BMD should be done to evaluate […]
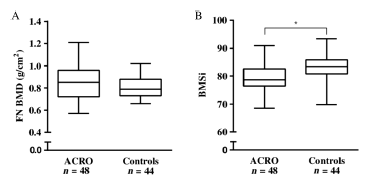
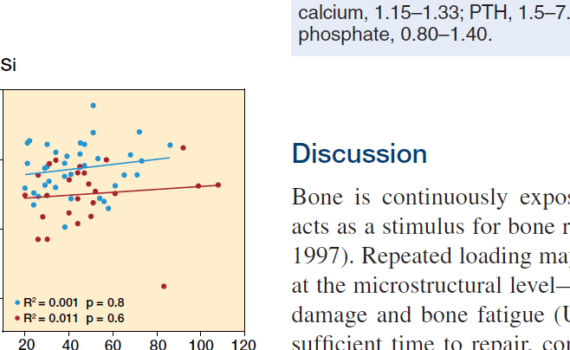
Abstract OBJECTIVE: Acromegaly is a rare disease caused by excess growth hormone (GH) production by the pituitary adenoma. The skeletal complications of GH and IGF-1 excess include increased bone turnover, increased cortical bone mass and deteriorated microarchitecture of trabecular bone, associated with a high risk of vertebral fractures in the […]
Abstract Osteoporosis is defined as a reduction in bone mass and impairment of bone quality that lead to bone fragility and fracture risk. Bone quality includes a hierarchy of properties from macroscopic to nanoscale level. Several techniques have been developed in an attempt to measure these non-density properties. Densitometry, high-resolution […]
Abstract Background and purpose — Bone fragility is determined by bone mass, bone architecture, and the material properties of bone. Microindentation has been introduced as a measurement method that reflects bone material properties. The pathogenesis of underlying stress fractures, in particular the role of impaired bone material properties, is still […]
Abstract Low bone mineral density (BMD) in HIV-infected individuals has been documented in an increasing number of studies. However, it is not clear whether it is the infection itself or the treatment that causes bone impairment. Microindentation measures bone material strength (Bone Material Strength index) directly. We recruited 85 patients, […]
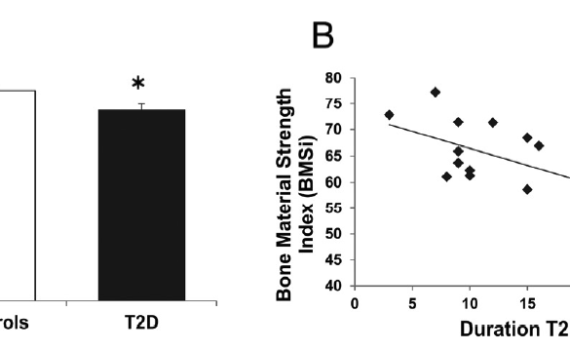
Abstract CONTEXT: Skeletal deterioration, leading to an increased risk of fracture, is a known complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). Yet plausible mechanisms to account for skeletal fragility in T2D have not been clearly established. OBJECTIVE: The objective of the study was to determine whether bone material properties, as […]
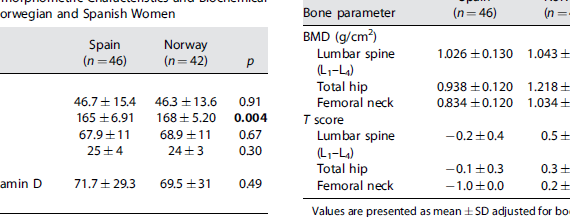
Abstract Hip fracture rates in Norway rank among the highest in the world, more than double that of Spanish women. Previous studies were unable to demonstrate significant differences between the two populations with respect to bone mass or calcium metabolism. In order to test whether the difference in fracture propensity […]
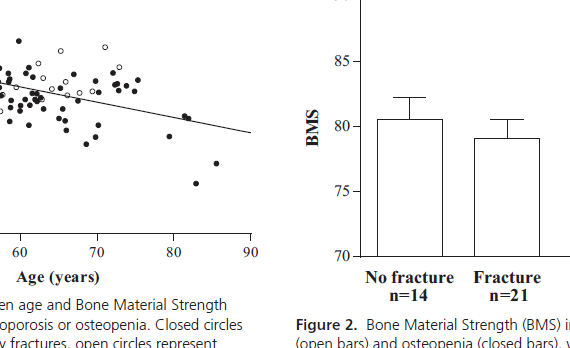
Abstract CONTEXT: Bone mineral density (BMD) does not fully capture fracture risk as the majority of fractures occur in patients with osteopenia, suggesting that altered bone material properties and changes in microarchitecture may contribute to fracture risk. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between bone material strength (BMS), […]
Abstract In an attempt to study the mechanical behavior of bone under indentation, methods of analyses and experimental validations have been developed, with a selected test material. The test material chosen is from an equine cortical bone. Stress-strain relationships are first obtained from conventional mechanical property tests. A finite element […]
Abstract We study the reference point indentation (RPI) technique which has a potential to directly measure mechanical properties of bone in patients. More specifically, we tested 6 month swine femoral cortical bone at mid-diaphysis region to investigate the effect of several testing variables on the RPI outputs. They include the […]
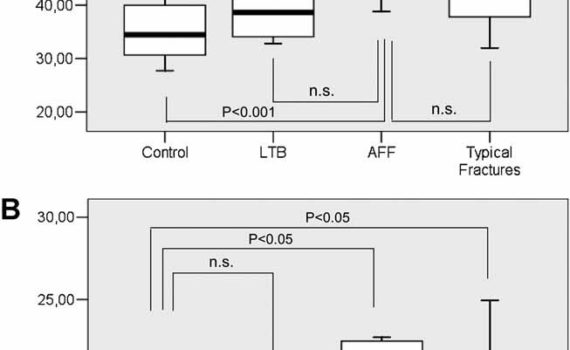
Abstract Atypical femoral fractures (AFF) associated with long-term bisphosphonates (LTB) are a growing concern. Their etiology is unknown, but bone material properties might be deteriorated. In an AFF series, we analyzed the bone material properties by microindentation. Four groups of patients were included: 6 AFF, 38 typical osteoporotic fractures, 6 […]